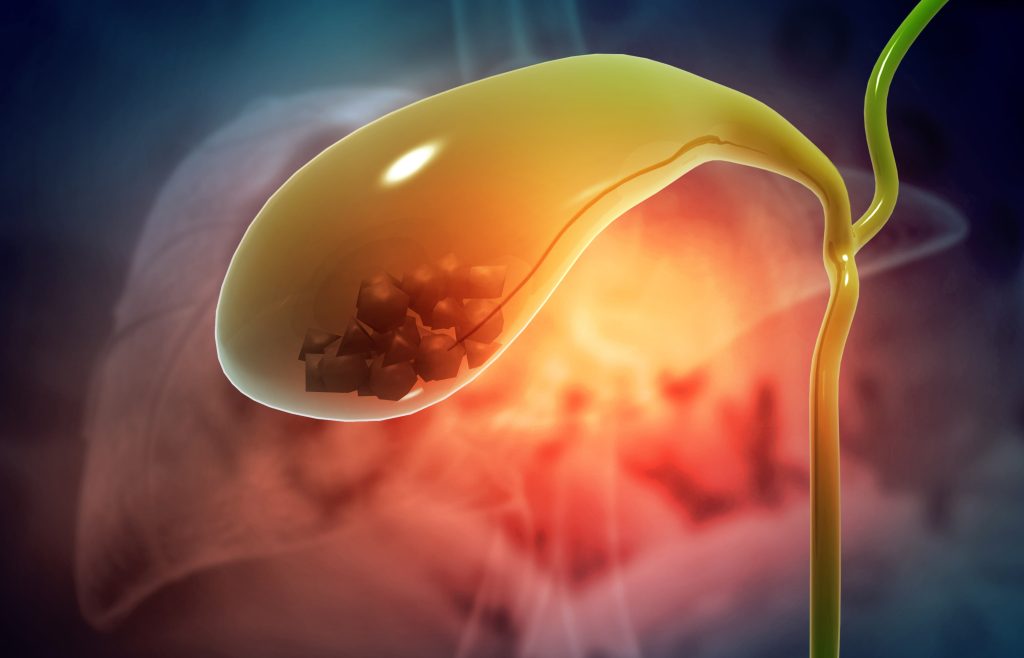
What are Gallbladder Stones?
Gallstones, also known as cholelithiasis, is a common condition in Singapore affecting women more than men. They are hardened deposits of bile substances that form in the gallbladder. The gallbladder is responsible for the storage and release of bile and aids in digesting fats in the food we consume.
Gallbladder stones are made up of hardened cholesterol or pigments such as bilirubin. These stones can vary in size, ranging from a tiny grain of sand to a golf ball. Many do not show any symptoms, and treatment is not required unless gallstone symptoms begin to develop. In certain cases, the gallbladder stone may block the bile duct, causing persistent pain and inflammation, and at times, the stone may travel towards the bile duct, blocking it and resulting in bile duct stones (choledocholithiasis).
What are the types of Gallbladder Stones?
Cholesterol Stones
Mainly composed of cholesterol, lecithin, and bile salts, these stones are the most common type of gallstones and are yellow-green in colour.
Pigment Stones
Made of bilirubin and calcium stones, pigment stones are small, dark and may appear brown or black in colour. They usually arise as a result of a high level of bilirubin in the system.
Mixed Stones
Mixed stones are formed by a combination of cholesterol and pigment gallstones that occur over time.
What causes Gallbladder Stones?
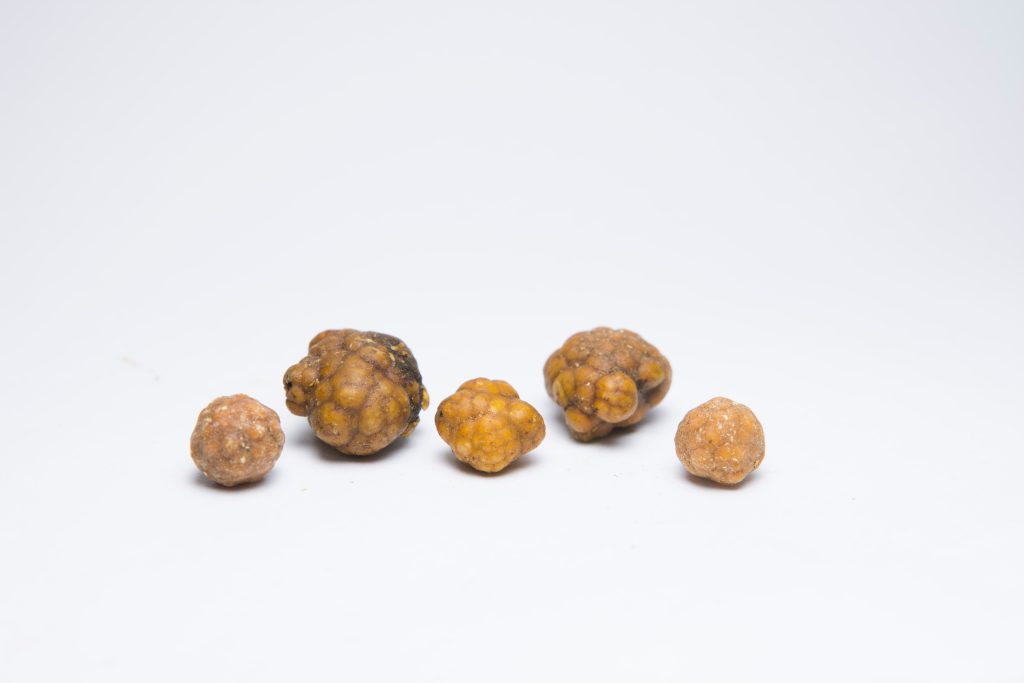

Gallbladder stones are formed when bile hardens into stone-like deposits. Although it is difficult to determine the exact reason why these changes in bile occur, it is generally believed to happen when the bile contains too much cholesterol, bilirubin or bile salts. Gallbladder stones also occur when the gallbladder does not empty completely.
What are the symptoms of Gallbladder Stones?
Usually gallbladder stones do not cause any symptoms, but some patients may present with the following gallstone symptoms:
- Sudden pain in the upper mid or upper right abdomen
- Pain in the right shoulder
- Pain between the shoulder blades
- Nausea or vomiting
- Jaundice
- Fever and chills
- Indigestion
- Belching
- Abdominal bloating
- Clay-coloured stools
How are Gallbladder Stones diagnosed?
There are several tests that can be used to diagnose gallbladder stones, such as:
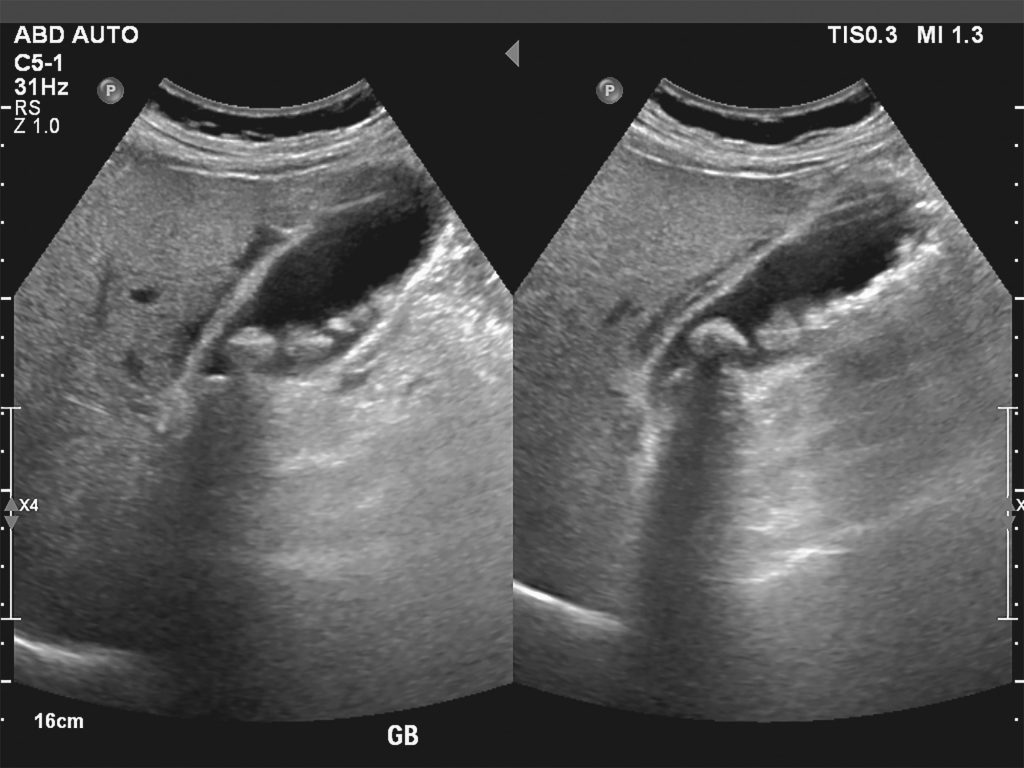
Ultrasound
Ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves that travel through body tissues to create images of the body structures and can be used to assess gallbladder stones.
Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP)
This test is similar to the ERCP procedure but uses magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) instead of a dye to visualise and provide detailed images of the bile ducts and stones, as well as the liver, gallbladder, and pancreas. Similarly, only stones found in the bile ducts can be removed.
CT scan
A CT scan can be used to capture X-ray images of your body, allowing your Gastroenterologist to detect the presence of calcified gallbladder stones or signs of inflammation in the pancreas, bile ducts, and gallbladder.
Blood tests
Your doctor may order a blood test in order to assess the presence of complications such as infection in the pancreas and any signs of bile duct blockage.
How are Gallbladder Stones treated in Singapore?
In most cases, gallstone treatment is not needed, unless the patient is in pain. Gallbladder stones can be treated through surgery or medications.
Surgery– Gallbladder removal surgery is known as cholecystectomy. It involves removing the entire gallbladder and is commonly performed if you are experiencing recurrent gallbladder stones. Once the gallbladder is removed, bile will flow directly into the small intestines instead of being stored in the gallbladder. The removal of the gallbladder does not affect your body’s ability to digest food, although you may experience diarrhoea.
Medications - Ursodiol can help dissolve the cholesterol present in gallbladder stones. However, it may take several months for the medication to dissolve it.
Does removing my gallbladder shorten my life?
No, removing your gallbladder will not lower your life expectancy. However, you are highly advised to make certain dietary changes, such as avoiding high-fat, fried and greasy foods initially.
What complications can arise if Gallbladder Stones are left untreated?
Although most gallbladder stones are asymptomatic, a small percentage of gallbladder stones may develop into something more serious. These complications include:
Cholecystitis
Cholecystitis occurs when the bile duct gets blocked causing bile to build up, resulting in infection and inflammation.
Increased risk of gallbladder perforation
If gallbladder stones are the cause of your gallbladder inflammation, it may put you at a higher risk of gallbladder perforation (tearing), potentially resulting in the rupture of the gallbladder.
Jaundice
The blockage of the gallbladder and/or bile duct may result in jaundice, a condition that causes a yellowish appearance of the skin and whites of the eyes as well as loose stools.
Acute pancreatitis
Acute pancreatitis is a severe condition that develops when the pancreas suddenly becomes inflamed. This can occur when a stone moves out of the gallbladder and blocks the opening of the pancreas, resulting in inflammation.
Dr Benjamin Yip advises patients to pay attention to gallbladder stones that are large (1 cm and above). This is because they are at an increased risk of gallbladder cancer and should have their gallbladder removed.
What diet is recommended to prevent Gallbladder Stones?
To prevent the formation of gallbladder stones, you may consider the following:
- Consume three balanced meals daily
- Maintain a normal weight
- Exercise regularly
- Reduce alcohol consumption
- Consume high-fibre foods
- Avoid refined carbohydrates and sugar
How can I temporarily relieve Gallbladder pain?
You can temporarily relieve gallbladder pain by:
- Reducing the consumption of fatty, oily and spicy foods
- Applying a warm compress to the affected region
- Exercising regularly; exercise can reduce cholesterol levels and prevent the formation of gallbladder stones.
When should I seek medical attention from a Gastroenterologist for my gallbladder stones?
If you have a medical history of gallstones or are experiencing symptoms like sudden and persistent abdominal pain, we advise you to consult a gastrointestinal specialist.
Summary
All in all, while gallbladder stones are not immediately life-threatening, it has the potential to progress into a more serious condition. Do seek immediate medical attention from a doctor if you are experiencing pain in your abdomen. We also highly recommend that you consult a Gastroenterologist to undergo regular health checkups. In addition, regularly exercising will go a long way in preventing the formation of gallbladder.
For specialised gallbladder stone care, book an appointment with Alpha Digestive Liver & Cancer Centre to consult our experienced Consultant Gastroenterologist Dr Benjamin Yip today!
References
- Cleveland Clinic (2021). Gallbladder: What Is It, Function, Location & Anatomy. [online] Cleveland Clinic. Available at: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/body/21690-gallbladder [Accessed 4 May 2022].
- Cleveland Clinic (2019). Gallstones: Treatment, Definition, Risk Factors & Symptoms. [online] Cleveland Clinic. Available at: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/7313-gallstones [Accessed 4 May 2022].
- NHS Choices (2019). Overview Gallstones. [online] NHS. Available at: https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/gallstones/ [Accessed 4 May 2022].
- Harvard Health Publishing (2011). What to do about gallstones - Harvard Health. [online] Harvard Health. Available at: https://www.health.harvard.edu/womens-health/what-to-do-about-gallstones [Accessed 4 May 2022].
- Mayo Clinic (2018). Gallstones - Diagnosis and treatment - Mayo Clinic. [online] Mayoclinic.org. Available at: https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/gallstones/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20354220 [Accessed 4 May 2022].
- Nall, R. (2020). Gallbladder pain: Treatments and home remedies. [online] www.medicalnewstoday.com. Available at: https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/gallbladder-pain#treatment [Accessed 4 May 2022].
- Penn Medicine. Gallstones. https://www.pennmedicine.org/for-patients-and-visitors/patient-information/conditions-treated-a-to-z/gallstones [Accessed 24 January 2024].

