What is Hepatitis C?
Hepatitis C is a viral infection that causes inflammation of the liver. While the virus itself does not damage the liver, liver damage occurs when the body’s immune system tries to fight it, and this can lead to severe complications like liver damage, liver scarring (cirrhosis), liver cancer and ultimately might cause death if left untreated.
How is Hepatitis C caused?
Hepatitis C is transmitted primarily through exposure to contaminated blood containing the virus when contaminated blood enters the bloodstream of an uninfected person. It can thus be spread by unsterile needles and equipment. It is contagious only through blood exposure, and cannot be transmitted through the air or the sharing of most household items that are unlikely to encounter blood.
What are the early signs of Hepatitis C?
Although the virus can mostly start off asymptomatic, it can cause acute symptoms one to three months after transmission. However, early symptoms may occur in some people. The early signs of Hepatitis C include:
- Stomach pain
- Dark urine
- Fatigue
- Fever
- Jaundice (yellow discolouration of skin and eyes)
- Worsened appetite
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Weight loss
Later symptoms of Hepatitis C
If the disease is not diagnosed and treated early, it can lead to further complications and more serious symptoms. These include:
- Ascites (fluid buildup)
- Hepatic encephalopathy (confusion, drowsiness, slurred speech)
- Easy bleeding/ bruising
- Itchy skin
- Spider angiomas (spidery blood vessels under the skin)
- Swollen legs
- Liver cancer
- Cirrhosis (scarring of the liver)
- Liver failure
When to visit the doctor
Once these symptoms appear or transmission is suspected, a doctor should be consulted for safety and assurance. It is also recommended to screen pregnant persons for the virus since there is a risk of transmission from the infected person to the fetus, and an increased risk of adverse fetal outcomes.
Is Hepatitis C serious?
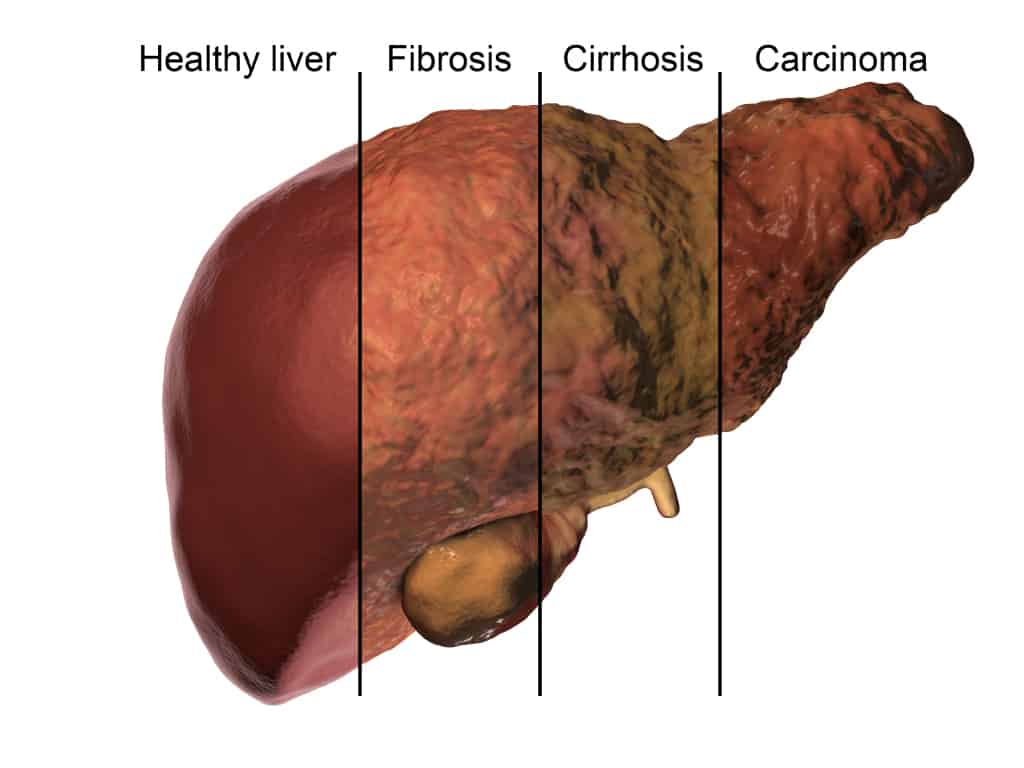
Hepatitis C can start off silently, but can cause serious complications and consequences if left untreated and thus is one of the most serious hepatitis viruses. However, the virus is treatable with antiviral drugs, and these medications can eliminate the virus completely.
Hepatitis C Treatment
Common antiviral drugs used to treat the virus include sofosbuvir and ledipasvir, which can be taken individually or together. It is also possible for the immune system to fight off acute Hepatitis C without treatment, but this occurs in less than half of the people who contract the virus.
Epclusa (sofosbuvir 400mg/velpatasvir 100mg) can also be prescribed to treat adults with chronic hepatitis C with or without cirrhosis. Patients generally have to take the drug everyday for a course of 12 weeks.
How is Hepatitis C diagnosed in Singapore?
The virus is diagnosed using a blood test called the HCV antibody test, which searches for antibodies that are released into the bloodstream of an infected person. If the test is positive, a liver function test or a liver fibrosis assessment may also be performed to check for liver damage and overall liver health.
How can you prevent Hepatitis C?
Hepatitis C currently does not have a vaccine that effectively prevents transmission, so prevention is dependent on reducing exposure risk in higher-risk populations, such as healthcare workers and people infected with HIV. It is important to employ the safe and appropriate use of injections and safe handling and disposal of sharp waste, and the prevention of exposure to blood during sexual intercourse.
Can you live with someone with Hepatitis C?
It is highly possible to live with someone who has Hepatitis C, since the virus is transmissible only by exposure to contaminated blood, and does not transmit through coughing, sneezing, or the sharing of household products like utensils.
Summary
To conclude, Hepatitis C can lead to severe complications in the long run, but is highly treatable and curable. If exposure is suspected, it is recommended to get tested in order to stay safe and healthy.

